Plate stone, do waterproof, open compartment...... From the han Dynasty "King of the mountain" home decoration to see the Han Dynasty to build French
Archaeology is like opening a blind box. Abundant modern archaeological achievements are the cornerstone of xuzhou Han culture research. Whether it is tomb archaeology or site archaeology, exploring the unknown world buried in soil is like opening a blind box, refreshing people's cognition again and again. 9f8757da6d0c1e9ad399d8aa46f222c0.jpg
The huge tombs of the King of Chu in the Western Han Dynasty, and the tombs of the brick and stone chamber in the Eastern Han Dynasty have provided important examples for understanding the construction engineering technology of the Han Dynasty, reflecting and representing the most advanced productivity, construction engineering technology, survey, planning and design and construction organization level at that time.
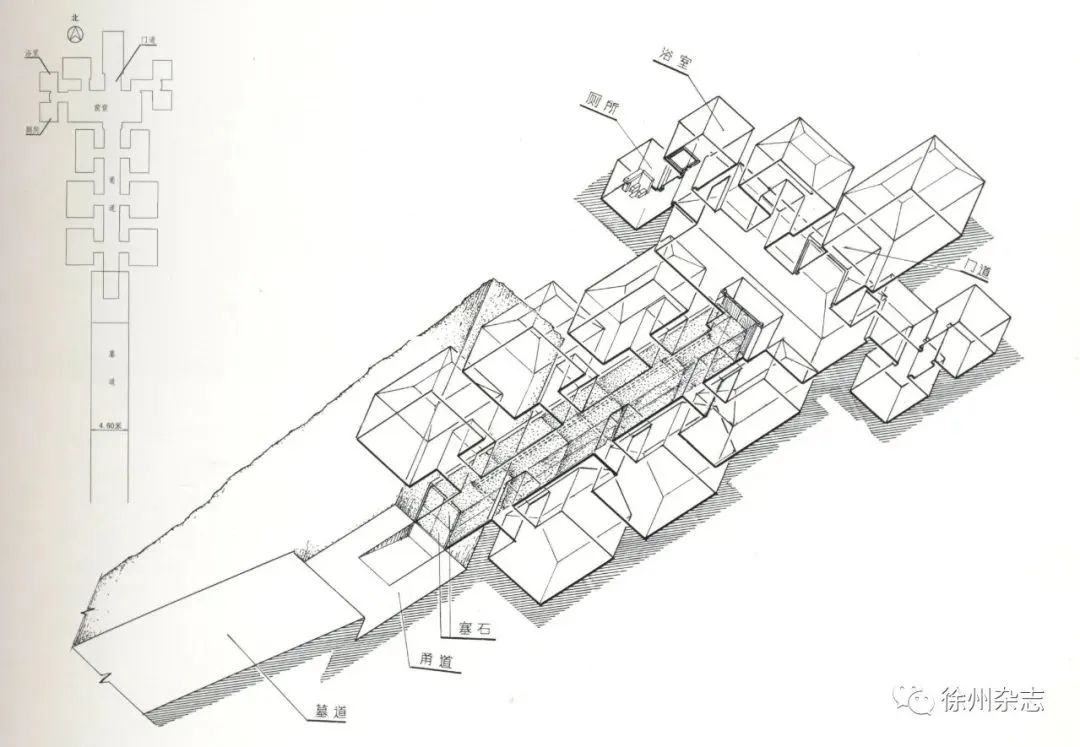


During the warring states period, the traditional holes in vertical hole of the tomb of box-type MuGuo space is very limited, burial hence gradually from ritual, to the space development of secular life, imitating YangZhai as far as possible, to build a bigger space. The central Plains area appeared some small cave tomb, completely changed the traditional shaft tomb shape system, so that yinzhai out of the first step towards three-dimensional space. However, the span, height and area of the soil caves are limited, and there is a danger of collapse, and their scale is far from meeting the needs of the upper ruling class.
Therefore, some vassal kingdoms of the Western Han Dynasty used the method of digging caves in the mountains, and built the mausoleum into a large horizontal cave tomb, "digging mountains for hiding" and "cutting mountains for coffin".
This kind of large transverse cave tomb is an unprecedented breakthrough to the funeral custom and funeral system at that time. It is undoubtedly a very huge project to excavate mountains and rock on such a large scale. It is the result of the development level of social productive forces at that time, the need and the possibility of adjusting measures to local conditions in some regions.
The picture
A clever suit to local conditions is a crafty master of nature
d20068147aeacf9d000405c5e2ddfc56.jpg
The geographical environment determines that the large cave tombs of Chu and other states have strong regional characteristics. These large cave tombs of princes of the Western Han Dynasty have been found mainly in Liang, Chu, Lu, Zhongshan and other states. Although some excavation reports (briefings) do not provide detailed geological information, according to the author's investigation, in fact, these tombs did not choose granite, sandstone or shale mountains, and were built on limestone mountains without exception.
Limestone is widely distributed in both north and south China, but it is by no means accidental that large cave tombs only appear in some areas north of huai River. The south is wet and rainy, limestone perennial water leakage, due to the chemical change of water participation and the formation of karst caves of different sizes, is not conducive to the excavation into a regular tomb shape, and the uneven force is easy to collapse. As a result, cave tombs were rarely seen in the southern kingdoms.
Compared with the south, there is less water and cold weather in the north of China, which is not conducive to the development of karst landforms. There are only natural damages mainly caused by physical factors such as fracture and collapse, which can be found mostly on the surface. The color of limestone is colorless and white, with moderate hardness, fine texture and suitable for excavating.
fabd9717f3d6098c079d274da972f851.jpg
Therefore, the use of cave tombs by the northern kingdoms in accordance with local conditions not only reflects the understanding of engineers and technicians of different climates and geography in the north and south of the Western Han Dynasty, but also reflects the understanding, scientific grasp and application of limestone geology and landform, of which chu is more typical and prominent.
In the Western Han Dynasty, Xuzhou was named the State of Chu with Pengcheng as its capital. The mountains around Pengcheng are undulating, and the room for choice is larger. In addition to the southwest of the capital, there are many peaks in all directions. The general direction of the tombs of emperors in the Western Han Dynasty had basic rules, but the direction of the large cave tombs of princes seemed to have no rules to follow.
The direction of the tomb in the Cave of King of Chu of the Western Han Dynasty in Xuzhou is east (King of Chu Mountain), west (Guishan, Huanshan), south (Lion Rock), north (Wonniu Mountain). The direction of this large cave tomb is different, no doubt related to the mountain situation, but more importantly also closely related to the rock trend.
c7b62c41d2f145d80f1ab0130de633db.jpg
The rock of each mountain has a certain trend, and the excavated rock tomb passage and tomb chamber to bear the huge pressure of the mountain, must make the direction of excavation and rock basic vertical, so that the rock pressure spread downward, make full use of rock mass to reach the maximum bearing capacity, not due to the same pressure caused by rock stripping. This shows that people had a good understanding of the geological structure inside the mountain, and a good understanding of the direction of the rocks.
In addition, the location of the mouth of the cave tomb was chosen to take into account the pressure required. Digging at the base of the mountain can reduce the cost of opening roads, transporting workers and food, water and tools, as well as the time needed to transport coffins and funeral goods during burial and other memorial ceremonies after burial. However, the mouth of the tomb of the King of Chu is invariably chosen at a moderate location close to the top of the mountain, which not only meets the requirement that the vertical and horizontal distribution of the tomb is basically on the same plane, but also minimizes the pressure of the rock mass on the tomb.
The palace of Chu in high imitation is fully functional
cd2ba14b4c494ea2ac30a39a6362cd11.jpg
Although the ground buildings of the Chu King's mausoleum garden have been destroyed by nature and man for over two thousand years, the underground tomb buildings imitate the various systems of royal family, army and county as much as possible. The heavy burial custom of han dynasty made the large cave tombs become the epitome of the palace architecture of the feudal kingdoms.
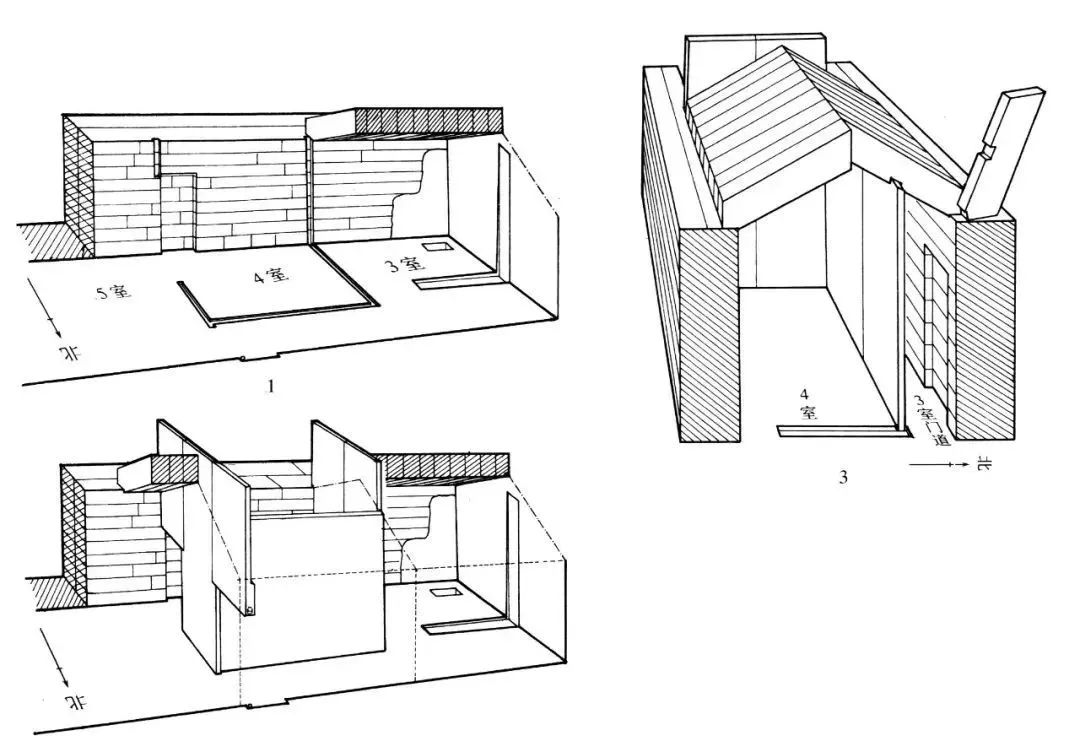
The roof of the tomb of Chu Wangyandong is of various forms, including flat roof, double slope roof, zigzag roof, 盝 roof, vault roof, double vault roof, four slope roof, four Angle spire roof and vault roof, which almost covers all the roof styles of today's buildings.
32fbcf0bfbb27165b8c7ffe6f777d4d3.jpg
The main tomb and the attached tomb of the King of Chu in Xuzhou Beidongshan mountain are modeled after the palace of the King of Chu and the inner court of the Palace of Chu built on the high platform respectively. The living facilities are complete, such as kitchen, well, kitchen room, wood room, mortar, ling Yin (ice cellar), music and dance court, armory, storehouse, toilet and so on.
Imitation does not mean mere imitation. In general, the height difference of ground buildings is mainly reflected in the aspect of high platforms, which are arranged on the same plane. However, in the cave tomb, there are multiple groups of buildings with different levels, and the buildings are even combined on two or three planes. General ground buildings and vertical pits and earth pits are arranged in a symmetrical axis, while the tomb of King Chu in Xuzhou Beidong Mountain has an asymmetric architectural layout, which is a breakthrough and innovation to the traditional architectural layout.
Chu king underground palace walls coated with cinnabon, so that the whole underground palace indoor a red, solemn and mysterious, both decorative effect and play the role of sterilization and anticorrosion, such as goat ghost mountain queen's tomb, north cave mountain tomb of chu King's main tomb, and even the bath are so. Combined with the historical records of "red on the flag, assisted by fire and Virtue", we have every reason to say that "Chinese red" had been formed in the early Han Dynasty more than two thousand years ago.
1651904431851112.jpg
1651904431125698.jpg
On the basis of the above decoration, some tombs are decorated with wooden boards and curtains. There are iron hooks in the four corners of the interior walls of room 11 beside the front hall of King Chu's tomb in Doulan Mountain. There are iron hooks in the four walls and the spines of several chambers of King Chu's tomb in Wuniu Mountain. The hook plays the role of curtain, which is mainly used for banquet guests or the king of Chu. Some of the roofs and walls of the tomb of the King of Chu in Woniushan have wooden decaying marks, indicating that the walls of the tomb were once decorated with panels.
Efficient scientific construction, durable and practical 09 f9d2a7ddd646eeaf35cc88e4be0533. JPG
The solid rock of the large cave tomb makes it possible to carve out a huge space, but the construction is difficult, and the technical content is far more than that of other tombs of princes in the same period.
Efficiency is one of the core of the project, in the Han Dynasty when tools and labor productivity were relatively low, the construction of mausoleum was sometimes an urgent project, how to improve the efficiency and careful organization of the problem is more prominent.
In order to rush the time and increase the efficiency of cave tomb excavation, it is not necessary to start from the front of the tomb ramp and then step by step when planning. According to the excavation of king chu's tomb in Lion Rock, the patio was excavated at first, then the back section and middle section of the tomb ramp were excavated, and finally the outer tomb ramp was excavated.
The side chambers of the two walls of the simple way in the tomb were not excavated from front to back, but were excavated in an all-round way by using the wide simple way, and the progress of excavation was not consistent. In this way, multiple working faces can be carried out simultaneously in the open-pit tomb ramp and the excavation of the tomb chamber to maximize efficiency.
f36444f96134d7bd549053daf827f70a.jpg
So far, there is no solution to how to keep accurate straight line in the mountain during the excavation of cave tomb. Taking the mausoleum of King Liu Zhu of Chuxiang in Guishan as an example, the college of Environment and Surveying and Mapping of China University of Mining and Technology measured with 3D laser scanning technology, the distance between 56 meters long corridors was 19 meters, and the error of the height of the two parallel corridors was only 5 mm. It would have been inconceivable to use a hammer chisel tool more than 2,000 years ago to achieve such precision on a very tight working surface.
In order to improve the efficiency, the tomb of King Yan Cave of Chu in the Western Han Dynasty used prefabricated architectural components, reflecting the technical level of prefabricated assembly at that time. In large cave tombs, the most representative one is the tomb of the Han and Chu Kings in Beidong, Shanxi Province, which uses stone prefabrication techniques including SLATE prefabrication, gabled roof prefabrication and trapezoidal beam prefabrication.
0818d7907f843bfc1bb6ca4cb23a7ddc.jpg
The large cave tombs of The King of Chu reflect that the science and technology of stone structure, performance and advantages had been fully understood at that time. The structure of the well of the attached chamber of king chu's tomb in Beidongshan was made of imitation wood, which shows that this technology appeared late in the early Western Han Dynasty.
The scientific design and careful construction have made the tombs of the princes of the Western Han dynasty still stable after more than two thousand years, which is the best proof of the technical level of construction engineering. To create such a miracle, it reflects the ingenuity and painstaking efforts of many craftsmen.
Superb drainage system, integrated
4c0913dfa52164ab6fd4f257977eab75.jpg
The large cave tombs of the King of Chu were all built on the mountainside. Every time there was a heavy rain, it would directly wash or even incline the rocks into the tomb ramp, which would cause silt and stones accumulation in the tomb ramp, and serious ones would cause casualties of the craftsmen and delay the construction period. Therefore, in the construction of the tomb of the King of Chu, the gutter above the tomb was built to intercept and divert rainwater.
For example, the tomb of the Empress of King of Chu in the mountain of burden basket is cut a "concave" shape ditch above the tomb ramp, which is lowered naturally according to the mountain. From the analysis of the phenomenon that the dam ditch of the tomb of the empress of Chu in Dousan Mountain has been built by ramming, its main function is waterproof in the construction process.
The tomb of the king of Chu in the early period was deep and long, and the water seepage from the tomb wall would not be less after rain. If there was a little extra water, it would pour into the tomb. Craftsmen in the pannier mountain slope in the king and queen's tomb near the aisle at the end of the end, digging out the first and the pyramid-shaped mound width, and the level of tunnel plane, then the plane down - and the aisle width, length and plane equal deep groove, groove with natural fractures, the pyramid-shaped mound, tunnel within the water can be collected by deep groove crack into the underground.
d71ba647a645f6d001dc3820fa80bad4.jpg
The craftsman keeps a large dip Angle when designing the whole tomb plane, that is, the tomb is high in the back and low in the front. By using the ground height difference and the dug waterway, the drainage ditch is chiseled along both sides of the floor of the interior walls and the floor of the corridor, so that the seepage water can be drained out of the corridor from back to front, from high to low and from inside to outside.
Such as guishan Chu King's tomb each chamber wall ground chiseled groove, groove width, depth are about 10 cm; The seepage water is collected in the grooves on both sides of the passage and discharged. Some drainage ditch light and dark combination, Wuniu Mountain tomb of the King of Chu in the tomb ground cut into the "King" shaped drainage ditch, placed in the ditch pebbles, through the doorway into a dark ditch.
In order not to make the tunnel or the top of the tomb water leakage sputtering, in the top of the water leakage water sink, connected to the wall water sink will lead to the ground. All sinks are inlaid with SLATE to keep them integrated with the roof and interior walls.
dbddcdaf9624545e651dc66faed6df39.jpg
All drainage facilities in the tomb except the ground are dark channels, some of which still function as water diversion. It is envisaged that these dark drainage channels should pass a rainy season inspection without leakage and ensure that the interior is dry before roof and wall decoration.
In the tomb of the King of Chu, there are not only drainage design of the whole tomb system, but also specific drainage measures, which constitute a thorough three-dimensional, rigorous and scientific drainage system of the whole tomb.